It is common for updates for more recent versions of Windows to be downloaded in the background and installed immediately upon reboot. As was recently the case with Windows 11 24H2, this is typically a good thing: the system stays current, security flaws are fixed, or useful new features and functions are implemented.
But occasionally, this is not even a positive thing: Occasionally, the system does not update, updates are only partially downloaded, or they are flawed from the start. Recently, this was the situation with Windows update KB5043145. The feared blue screen of death (BSOD) was all that some users saw instead of exciting new features and optimizations.
You should first remove the problematic “upgrade” from your computer if there are issues with a Windows update. Microsoft frequently fixes these issues quickly, and the next Windows update (the update to the update, as it were) resolves the issue.
You can keep using the “old” version of Windows until then without encountering any issues or accepting any special risks. We outline many quick and easy methods for resetting a Windows update.
Checklist before restoring
In the event of update issues, you should review this checklist to rule out common issues and conflicts:
- Make sure that there is enough space on the system hard drive for updates.
- Restart the system to see whether updates can then be installed correctly.
- Run the Windows update again if necessary.
- Disconnect external hardware such as drives or storage media that are not required for system operation.
- Check the Device Manager to see if any conflicts or errors are reported.
- Make sure that no virus or malware scanners are torpedoing the update. Such programs may need to be temporarily uninstalled.
- Check whether the Windows service for updates is activated: Click on Start and enter services.msc. Click on the first hit (“Services”) and search for “Windows Update” at the bottom of the list. The startup type must be set to “manual;” this can be adjusted by right-clicking and then selecting “Properties.”
Here’s how to reset or fix Windows updates if these methods do not work.
Windows system tool for troubleshooting
Microsoft is also conscious that its own upgrades might occasionally cause issues with the operating system. Therefore, options to resolve update issues or reset updates are included with modern versions of Windows. The simplest approach is to use Windows’ built-in update troubleshooting feature, which varies based on the operating system.
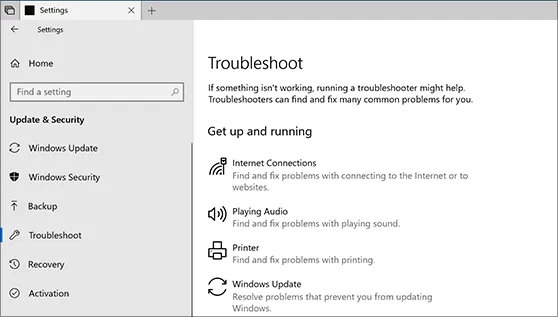
To access “Other troubleshooters” in Windows 11, navigate to Start > Settings > System > Troubleshoot. You can launch the troubleshooter by using the “Run” command that is located next to the “Windows Update” entry. After that, a system restart is advised.
In Windows 10: Go to Start > Settings > Update & Security and select “Troubleshooting” As an alternative, click Start, type troubleshooting, and choose “Troubleshooting settings” as the first entry. We now choose the “Additional troubleshooting” entry, which is at the bottom in both situations. The “Windows Update” field will then appear on the left-hand side of the next window. Clicking on it will display the “Run troubleshooter” option. After clicking on it, wait for the system to finish evaluating and fixing the error, if needed, and then restart.
System restore point
If you do not explicitly stop the process, Windows frequently generates restore points that can be used to return the system to a previous configuration. No data or settings are lost, and this can help with upgrades as well as a host of other OS annoyances. Such restoration points can also be manually specified by users.
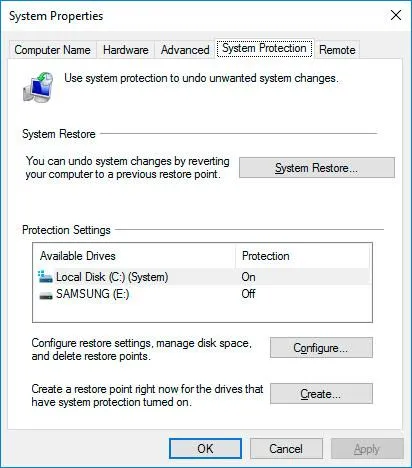
How to activate a restore point:
- Tap on Start and enter restore point there. The first hit should now be “Create restore point,” click on the entry.
- In the window that opens (tab: “System protection”), select the field “System Restore…”(see image).
- Click on “Next” in the new window.
- Windows displays a list of available restore points, select the desired entry. Tip: You can use the “Search for affected programs” command to check in advance which components are affected by the restore.
- Confirm your selection and click on “Next” and “Finish.” You may need to confirm a security notice. The system will now be reset to the configuration of the restore point and restarted.
Reset Windows Update Tool
Certain software issues require additional software to resolve: For instance, with the Reset Windows Update Tool. The linked page offers a portable version (archive) of the free open source program for download. Following the download:
- Unzip the tool into a folder of your choice.
- Start “wureset.exe” with admin rights. (Right-click and the command “Run as administrator”).
- Select the program language.
- In the next step, select “Restore Windows Update Components” (usually “2” and ENTER).
- The process may take several minutes. Updates should then work again.
Install updates manually
You can occasionally assist manually by downloading and installing the problematic update yourself if the automatic Windows update fails because of an update. For instance, you can download crucial updates after restoring to a previous restore point without using Windows’ built-in update feature to restore the problematic update that you wish to reset.
However, in order to accomplish this, you must be aware of the update’s identity (KB number). Advice: Prior to installation, the update IDs of new updates are frequently shown via “Windows Update.” Just type “Check for updates” into the Start menu and choose the corresponding option. You can also search for the update in question under “Show update history” to see all of the earlier releases along with their titles if you are unable to locate it there.
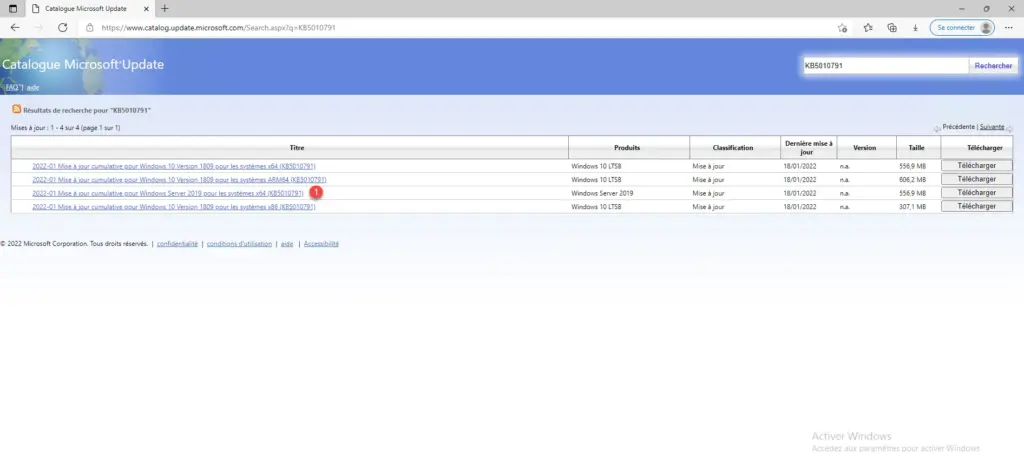
- Then visit the Microsoft update catalog and enter the KB identifier in the search field.
- Download the affected update yourself.
- Start the update in your download folder.
Reset and restart update services
Update services can be stopped and restarted via the command prompt. Updates cannot be reset using this method, however you can assist the operating system if it does not update. Follow these steps:
- Click on Start and enter cmd.
- Right-click on the top hit “Command Prompt” to run the prompt as administrator.
- Then enter these commands one after the other:
net stop bits
net stop wuauserv
Dism.exe /online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanupsfc /scannow
net start bits
net start wuauservWuauserv (Windows Update AutoUpdate Service) and BITS (Intelligent Background Transfer Service) will be stopped and restarted as a result. Now you can try installing the troublesome update once more.
System reinstall
Reinstalling Windows may be an option if none of the actions outlined here result in the desired outcome. You should only do this as a last option because it may cause you to lose a lot of settings and data: For instance, if an update causes the system to stop functioning (properly) and you are unable or unwilling to wait for a Microsoft repair.